Blog #3 - Solar vs. Diesel: Which Yacht Suits Your Sustainable Lifestyle?
ContentsIntroduction
Key Point 1: Cost Comparison – Evaluating the Financial Landscape
Key Point 2: A Decade of Ownership – Long-Term Cost and Emissions Analysis
Key Point 3: Environmental Impact – Sailing Towards Sustainability
Key Point 4: Solar-Electric Yachting's Transformative Potential
Conclusion
IntroductionIn our last post, we introduced the revolutionary world of solar-electric propulsion and its potential to transform the yachting experience. Today, we’ll take this discussion a step further by comparing solar-electric yachts to their diesel-powered counterparts.
Imagine yourself aboard a luxurious catamaran, anchored in a tranquil bay. The only sounds you hear are gentle waves and seabirds calling in the distance, while solar panels power every onboard system. Now contrast this with the hum of a diesel generator disrupting that serenity, powering appliances while emitting fumes and noise.
Your choice between a solar-electric and diesel-powered yacht isn’t just technical—it reflects your values. Do you prioritize sustainability, long-term efficiency, and quiet operation, or stick with traditional options? In this article, we’ll explore the financial and environmental impacts of this decision, guiding you to the option that aligns best with your lifestyle and aspirations.
key point 1Cost Comparison – Evaluating the Financial Landscape
The Initial Investment: Assessing Upfront Costs
At first glance, a diesel-powered catamaran may seem like the more cost-effective option. Its initial purchase price is often lower than that of a solar-electric yacht. However, that difference stems from the advanced technology powering solar-electric yachts, including lithium-ion batteries, expansive solar arrays, and integrated energy management systems.
While the upfront cost of a solar-electric yacht may seem steep, think of it as an investment. Over time, reduced fuel consumption, lower maintenance requirements, and higher resale value make solar-electric yachts a smart financial choice, especially if you’re planning for long-term ownership.
Operational Costs: Long-Term Financial Implications
As you weigh your options, it’s crucial to consider ongoing expenses:
Diesel-Powered Catamarans:
Fuel Costs: Diesel fuel prices fluctuate, but a diesel-powered catamaran typically consumes 40–60 liters per hour when cruising. Generators running at anchor add further fuel costs.
Maintenance Costs: Regular servicing, such as oil changes, filter replacements, and engine overhauls, can lead to significant annual expenses.
Solar-Electric Catamarans:
Fuel Savings: Solar-electric yachts rely primarily on renewable energy. Although equipped with a backup generator, its use is minimal, drastically reducing fuel costs.
Lower Maintenance: Electric propulsion systems have fewer moving parts than diesel engines, translating to fewer breakdowns and lower maintenance costs.
While the day-to-day costs of fuel and maintenance paint a clear picture of operational savings, a broader view emerges when considering the total cost of ownership over a decade. Beyond economics, how do these yachts perform in terms of emissions and value retention as they age? Let’s take a deeper look.
Key Point 2A Decade of Ownership – Long-Term Cost and Emissions Analysis
Assumptions for Usage and Operational Patterns
To create a realistic comparison, imagine spending 14 weeks a year aboard your yacht, with a mix of cruising and time spent at anchor. Here’s what that looks like:
Total Time Spent on Board per Year: 14 weeks (2,352 hours).
Cruising Time:
Diesel Catamaran: 364 hours (15.5% of total time) at 11 knots cruising speed.
Solar Electric Catamaran: 533 hours (22.7% of total time) at 7.5 knots cruising speed.
Time at Anchor or in Marina:
Diesel Catamaran: 1,988 hours.
Solar Electric Catamaran: 1,819 hours.
Cruising Distance: Both yachts cover 4,000 nautical miles annually.
Generator Specifications for Solar-Electric Catamaran: A 140 kW diesel generator consuming 21 liters/hour, operating during 1/3 of cruising time (177 hours annually).
Diesel Powered Catamarans Diesel Generator Consumption at Anchor: Between 5 and 10 liters/hour, depending on load.
What Do 4,000 Nautical Miles Represent?
To put this distance into perspective:
Short-Distance Routes:
28 round trips between Palma de Mallorca and Ibiza.
50 round trips between Cannes and Saint-Tropez.
Medium-Distance Routes:
Approximately 10 round trips between Miami and Nassau in the Bahamas.
13 round trips between Fort Lauderdale and Key West.
Around 15 round trips between Athens and Santorini.
Diesel-Powered Catamaran: Emissions and Costs
Fuel Consumption:
Cruising: At speeds of 10–12 knots, expect to consume 40–60 liters of diesel per hour.
Lower Estimate: 364 hours × 40 liters/hour = 14,560 liters.
Upper Estimate: 364 hours × 60 liters/hour = 21,840 liters.
At Anchor: Even when stationary, the onboard generator powers essential systems like air conditioning and refrigeration, consuming 5–10 liters of diesel per hour.
Lower Estimate: 1,988 hours × 5 liters/hour = 9,940 liters.
Upper Estimate: 1,988 hours × 10 liters/hour = 19,880 liters.
Total Annual Fuel Consumption:
Lower Estimate: 24,500 liters.
Upper Estimate: 41,720 liters.
Annual CO₂ Emissions:
Diesel fuel generates 2.68 kilograms of CO₂ per liter burned. Using this metric:
Lower Estimate: 24,500 liters × 2.68 kg CO₂/liter = 65,660 kg CO₂ annually.
Upper Estimate: 41,720 liters × 2.68 kg CO₂/liter = 111,809 kg CO₂ annually.
Solar-Electric Catamaran: Emissions and Costs
Fuel Consumption and Operational Patterns:
Solar-electric catamarans are designed to minimize reliance on fossil fuels by utilizing advanced solar panels, large-capacity batteries, and efficient energy management systems. However, a backup diesel generator is included for specific scenarios, such as extended cruising or prolonged periods of low sunlight.
Cruising:
At speeds of 7.5 knots, the solar-electric catamaran primarily uses stored solar energy from its batteries. The backup generator operates during 1/3 of cruising time to recharge the batteries.Annual Generator Fuel Consumption During Cruising:
Generator Runtime: 533 cruising hours × 1/3 = 177 hours.
Generator Consumption: 177 hours × 21 liters/hour = 3,731 liters.
At Anchor:
During time spent at anchor, the catamaran's onboard energy needs are fully met by solar panels and batteries. No generator use is required, ensuring silent and emission-free operation.Total Annual Fuel Consumption:
Annual Fuel Consumption: 3,731 liters.
Annual CO₂ Emissions:
Using the same metric for diesel fuel emissions (2.68 kilograms of CO₂ per liter burned):
CO₂ Emissions: 3,731 liters × 2.68 kg CO₂/liter = 9,999.08 kg CO₂ annually.
Comparison to Diesel-Powered Catamarans
When compared to diesel-powered catamarans, the solar-electric alternative demonstrates an 84%–91% reduction in fuel consumption and CO₂ emissions annually. This stark contrast underscores the environmental and cost advantages of solar-electric technology, particularly for owners prioritizing sustainability and operational efficiency.
Comparison Summary
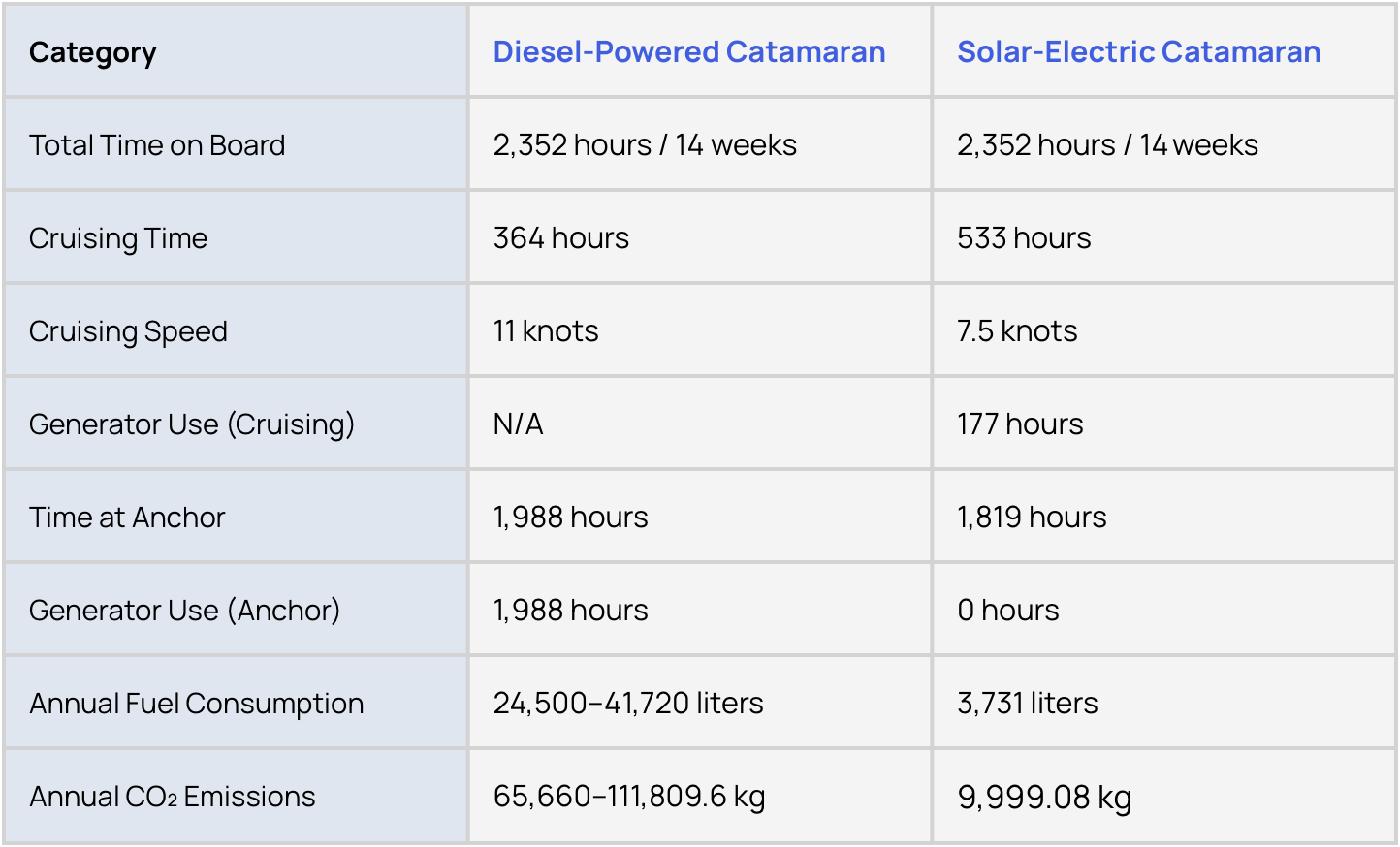
The following table provides a side-by-side comparison of the operational patterns, fuel consumption, and emissions for a 60-foot diesel-powered catamaran and a solar-electric catamaran:
Key Insights from the Comparison
Fuel Consumption:
The diesel-powered catamaran consumes between 24,500 and 41,720 liters annually, depending on operational patterns, while the solar-electric catamaran consumes only 3,731 liters, representing an 84%–91% reduction.
CO₂ Emissions:
A diesel-powered catamaran emits between 65,660 and 111,809 kilograms of CO₂ annually, compared to just 10.000 kilograms for the solar-electric alternative, showcasing the environmental benefits of renewable energy systems.
Efficiency at Anchor:
Solar-electric catamarans require no generator use at anchor, offering silent and emission-free operation, whereas diesel-powered catamarans depend heavily on their generators to power onboard systems.
Cost and Environmental Benefits:
The solar-electric catamaran significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels, leading to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious owners.
Value Retention and Future-Proofing: The Long-Term Edge of Solar-Electric Catamarans
When evaluating the cost of ownership for a 60-foot diesel-powered catamaran versus a similarly sized solar-electric catamaran over a decade, one critical factor often overlooked is how each type of yacht retains its value and adapts to technological advancements. Unlike diesel-powered yachts, solar-electric catamarans can be upgraded incrementally or comprehensively at any time, offering unique advantages for long-term ownership.
Diesel-Powered Catamarans: Traditional diesel-powered catamarans generally experience a steady decline in value over time. Industry data suggests that yachts can lose up to 40% of their initial value within 8–10 years, depending on usage and maintenance. After 8 years, these vessels often require significant overhauls, such as replacing or upgrading large diesel engines. This process is not only technically complex and costly but also comes with diminishing returns.
Additionally, diesel catamarans are constrained by the stagnation in diesel engine technology. Over the last century, diesel engines have reached their practical limits, and significant advancements in efficiency or performance are unlikely. This limitation contrasts sharply with the rapid innovation occurring in renewable energy and electric propulsion systems.
Diesel catamarans are also likely to face reduced demand in the resale market as sustainability becomes a dominant buyer preference. Stricter emissions regulations and evolving expectations are expected to make traditional diesel yachts less appealing to environmentally conscious buyers by 2030.
Solar-Electric Catamarans: Solar-electric catamarans, in contrast, not only retain value better but can also increase in functionality and appeal over time due to advancements in key technologies. After any period of time—whether it’s 4, 8, or 12 years—solar-electric yachts can be upgraded with state-of-the-art batteries and solar panels, resulting in a vessel that performs better than when it was originally purchased.
This ability to integrate cutting-edge advancements in energy storage and solar efficiency ensures that solar-electric yachts remain relevant and competitive. Owners benefit from lower costs for future upgrades and an enhanced resale value as sustainability and renewable energy continue to grow in importance.
(For detailed insights into the specific technological advancements driving these changes, refer to the section "Technological Advancements Driving the Change" further below.)
These advancements allow solar-electric yachts to remain competitive in the resale market, even after significant use. As sustainability becomes a top priority for buyers, a solar-electric yacht upgraded with the latest technology stands out as a cutting-edge vessel, appealing to eco-conscious buyers and retaining—or even increasing—its value.
Operational savings and value retention are just part of the equation. The choice between solar-electric and diesel-powered yachts also carries profound environmental implications, affecting not only your carbon footprint but also the ecosystems you explore. Here’s how the two compare when it comes to sustainability.
Disclaimer: Simplified Assumptions and Comparative Framework
The calculations and comparisons in this blog are based on simplified assumptions and generalized scenarios. For example, the estimated annual cruising distance of 4,000 nautical miles is above average for many yacht owners and can vary significantly depending on individual usage patterns. Additionally, the analysis contrasts a purely diesel-powered catamaran with a purely solar-electric catamaran, excluding hybrid solutions, which hold significant merit and are already influencing the market. We have also assumed that the solar array installed on the solar-electric yacht is sufficient to power household systems during time at anchor, which may not always be the case for every 60-foot solar-electric catamaran.
In the case of the diesel-powered catamaran, it should also be noted that fuel consumption figures of 40–60 liters per hour at cruising speed typically refer to propulsion only. In reality, additional fuel consumption can result from onboard generators running household appliances or from alternators connected to the propulsion engines producing electrical power.
This blog provides a comprehensive analysis based on current data and trends. We understand that every yacht owner's needs and circumstances are unique. We are happy to provide tailored advice and further insights to help you navigate your decision-making process. This analysis focuses on running costs, resale value, and environmental impact and is intended to provide a foundational understanding for comparing propulsion technologies.
Key Point 3Environmental Impact – Sailing Towards Sustainability
A Tale of Two Systems
As described in the introduction already, now picture yourself again anchoring in a pristine bay. On your solar-electric catamaran, silence envelops you as sunlight powers everything onboard. Contrast this with a diesel-powered yacht, where the hum of a generator disrupts the peace and emits harmful fumes.
This isn’t just about personal experience—it’s about protecting the planet. Solar-electric catamarans significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and noise pollution, preserving marine ecosystems while aligning with future regulations.
Carbon Emissions: A Comparative Analysis
Diesel-Powered Catamarans:
Diesel-powered yachts rely entirely on fossil fuels, making them significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Burning diesel generates approximately 2.68 kilograms of CO₂ per liter of fuel, according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Based on the operational patterns outlined earlier:
Annual CO₂ Emissions:
Lower Estimate: 65,660 kilograms of CO₂.
Upper Estimate: 111,809 kilograms of CO₂.
Solar-Electric Catamarans:
Solar-electric yachts are designed to minimize reliance on fossil fuels. With limited use of a backup generator during cruising and no generator use at anchor, solar-electric catamarans emit approximately 10.000 kilograms of CO₂ annually.
This represents an 84%–91% reduction in emissions compared to their diesel-powered counterparts.
Note on Life-Cycle Emissions
This comparison focuses solely on operational carbon emissions during the lifetime of the yachts. It excludes life-cycle emissions such as:
— The production of batteries, solar panels, and diesel engines.
— The extraction, refining, and transportation of diesel fuel.
A separate blog will delve into these aspects, providing a comprehensive view of the environmental footprint of both propulsion systems.
Preserving Marine Ecosystems
Diesel-Powered Catamarans:
Noise Pollution: The constant hum of diesel engines and generators disrupts the natural acoustic environment, affecting marine species such as dolphins and whales that rely on sound for communication, navigation, and mating.
Exhaust and Water Contamination: Diesel engines release exhaust gases containing harmful substances such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and particulate matter. These can react with seawater, degrading water quality and harming marine ecosystems. Additionally, small leaks or unburned fuel during operation can introduce pollutants into the water.
Oil and Fuel Pollution During Refueling: Even minor spills during refueling can have devastating consequences for fragile marine ecosystems, contaminating water and harming wildlife.
Solar-Electric Catamarans:
Silent Operation: With electric propulsion systems, solar-electric yachts glide through the water with minimal noise, allowing for a more harmonious interaction with marine life.
Reduced Risk of Fuel Contamination: Although solar-electric catamarans occasionally rely on backup generators, their minimal fuel usage significantly reduces the risk of fuel spills and water contamination compared to diesel-powered vessels.
Future-Proofing: Aligning with Environmental Regulations
The maritime industry is undergoing a seismic shift toward sustainability, with regulations such as the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) Greenhouse Gas Strategy mandating a 50% reduction in maritime emissions by 2050. Diesel-powered yachts will face increasing challenges to comply with these tightening restrictions, likely requiring expensive retrofits or operational changes.
In contrast, solar-electric catamarans are inherently aligned with these goals, offering owners a future-proof choice that not only complies with emerging standards but sets a benchmark for sustainable yachting.
Case Study: Emissions Saved Over a Decade
By transitioning from a diesel-powered to a solar-electric catamaran, an owner can achieve substantial environmental benefits over 10 years:
CO₂ Emissions Reduction: Savings of approximately 555,000 to 1,017,000 kilograms of CO₂—equivalent to taking 120 to 220 cars off the road for an entire year.
Fuel Savings: Preventing the combustion of over 210,000 liters of diesel fuel.
Ecosystem Benefits: Reduced noise pollution and cleaner waters contribute to healthier marine environments, benefiting both wildlife and yacht owners who enjoy unspoiled natural beauty.
(This comparison assumes that a typical passenger vehicle emits between 3,500 and 4,600 kilograms of CO₂ annually, based on standards from the European Environment Agency and the U.S. EPA. The range reflects regional differences in vehicle emissions, which depend on fuel efficiency and average usage.)
Key Takeaways from Environmental Impact
A Clear Environmental Advantage: Solar-electric catamarans significantly reduce emissions and environmental impact, aligning with the values of eco-conscious yacht owners.
A Better Experience for Wildlife and Owners: The silent operation of solar-electric yachts enhances the experience for owners and preserves delicate marine ecosystems.
Prepared for the Future: Solar-electric yachts are inherently aligned with the yachting industry’s move toward sustainability, making them a forward-thinking investment.
As we navigate the growing importance of sustainability, it’s clear that solar-electric yachts are not just an eco-friendly choice today—they’re also a glimpse into the future of yachting. Rapid advancements in technology and shifting market trends are reshaping the industry. Let’s explore what lies ahead for solar-electric propulsion.
Key Point 4Solar-Electric Yachting's Transformative Potential
Technological Advancements Driving the Change
The solar-electric yachting industry is accelerating into a future shaped by rapid innovation, with advancements in key technologies enhancing performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
1. Battery Technology:
Energy Density Improvements:
Lithium-ion batteries are projected to achieve up to 65% greater energy density over the next decade, allowing for smaller, lighter battery systems with longer cruising ranges (Source: McKinsey & Company).Faster Charging:
Improved charging technologies are significantly reducing downtime, enabling solar-electric yachts to recharge more efficiently, even during brief marina stops.Cost Reductions:
Prices for lithium-ion batteries have dropped by nearly 89%, from $1,191 per kWh in 2010 to $132 per kWh in 2023, according to BloombergNEF. While marine-grade battery systems may not have experienced the exact same price trajectory, the trend strongly benefits solar-electric yachts, enabling more affordable and efficient upgrades. These advancements make solar-electric systems increasingly accessible to a broader range of yacht owners.
2. Solar Panel Efficiency:
Efficiency Gains:
Solar panel efficiency has steadily improved, increasing by approximately 0.5% annually over the last decade. Top-tier panels now exceed 25% efficiency (Source: National Renewable Energy Laboratory). Breakthroughs, such as Fraunhofer ISE's 47.6%-efficient quadruple solar cell, highlight the potential for reaching efficiencies of up to 50% in the coming years (Source: Fraunhofer ISE). However, translating these advancements into commercially viable and cost-effective solutions for marine applications remains a challenge.Cost Declines:
Solar panel costs have fallen by over 88% since 2013, as reported by IRENA, driven by mass production and advancements in manufacturing techniques.Innovative Designs:
Flexible, semi-transparent, and lightweight panels are expanding the possibilities for solar integration, allowing for seamless installation across curved or unconventional surfaces without compromising aesthetics.
3. Smart Energy Management Systems:
AI-Driven Optimization:
The adoption of AI-driven energy management systems is revolutionizing how solar-electric yachts optimize power distribution, monitor performance, and predict energy needs.Real-Time Diagnostics:
These systems can remotely monitor energy usage, battery health, and solar output, reducing maintenance costs and maximizing efficiency.
Market Trends: The Rise of Solar-Electric Yachting
As environmental awareness grows, solar-electric yachting is transitioning from a niche market to a prominent force in the industry.
Changing Consumer Priorities:
Today’s yacht buyers increasingly value emissions reduction, quiet operation, and the freedom to explore remote destinations without depending on fossil fuels.Adoption Across Sectors:
Private Owners: Solar-electric catamarans are becoming a favored choice among eco-conscious individuals seeking luxury aligned with their values.
Charter Industry: Solar-electric yachts are an attractive option for travelers seeking unique, sustainable experiences. Charter companies are capitalizing on this trend, incorporating these vessels into their fleets to cater to a growing demand for greener vacations.
Commercial Applications: Beyond private use, solar-electric systems are gaining traction in commercial sectors, including ferries and workboats, further demonstrating their scalability.
Strong Market Growth:
The global electric boat market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12%, fueled by advancements in renewable technology and changing consumer priorities (Source: Allied Market Research).
Government incentives and subsidies are further reducing entry barriers for manufacturers and buyers alike, driving adoption across private, charter, and commercial sectors.
The Role of Regulations and Sustainability Initiatives
As the yachting industry embraces sustainability, solar-electric yachts naturally align with current and future regulations:
Regulatory Push:
Policies such as the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) 2050 Greenhouse Gas Strategy call for a 50% reduction in maritime emissions, putting pressure on traditional diesel-powered yachts to adapt.
Ports and marinas are increasingly investing in renewable energy infrastructure, further supporting the practicality of solar-electric systems.
Sustainability as a Selling Point:
Solar-electric yachts represent a compelling intersection of luxury and environmental responsibility, appealing to a new generation of buyers who prioritize experiences that align with their eco-conscious lifestyles.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the future is bright, certain challenges remain for the solar-electric yachting industry. Addressing these issues presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth.
Battery Recycling and Resource Management:
Efficient recycling systems for lithium-ion batteries will be critical to reducing the lifecycle environmental impact of solar-electric yachts.Infrastructure Expansion:
As adoption grows, the need for renewable energy infrastructure in marinas worldwide will become increasingly important to ensure seamless operations.Performance Enhancements:
Current limitations in speed and range compared to traditional diesel yachts offer an opportunity for manufacturers to innovate and close the gap.Opportunities for Differentiation:
Customization and advanced designs will allow manufacturers to stand out in an increasingly competitive market.
Superior user experiences, enhanced by AI and automation, will further distinguish solar-electric yachts.
The future of solar-electric yachting is about more than reducing emissions; it’s about setting a new standard for what yachting can be. By harmonizing sustainability, innovation, and luxury, solar-electric yachts represent a bold step toward a cleaner, quieter, and more inspiring maritime experience.
ConclusionConclusion
The Choice Between Tradition and Innovation
The decision between a diesel-powered and solar-electric catamaran goes far beyond technical specifications. It reflects your values as a yacht owner, charterer, or eco-conscious adventurer. Diesel-powered yachts, while rooted in decades of tradition and engineering, are increasingly at odds with the growing demand for sustainability, efficiency, and environmental stewardship.
Solar-electric yachts, on the other hand, represent the forefront of innovation, offering a cleaner, quieter, and more efficient way to explore the seas. They provide not only a tangible reduction in carbon emissions and fuel costs but also a unique experience that harmonizes luxury and sustainability.
Key Takeaways
Cost Efficiency Over Time:
While solar-electric catamarans have higher upfront costs, their long-term savings in fuel and maintenance make them an economically viable choice for forward-thinking yacht owners.Environmental Impact:
The dramatic reduction in CO₂ emissions and elimination of noise pollution position solar-electric yachts as the ideal choice for preserving marine ecosystems and aligning with global sustainability goals.Future-Proof Investment:
Solar-electric catamarans are inherently aligned with the maritime industry's shift toward greener technologies, offering compliance with future regulations and higher resale values as the demand for sustainable solutions grows.Evolving Technology:
With advancements in battery efficiency, solar panel design, and AI-driven energy management, the performance gap between solar-electric and diesel-powered yachts continues to narrow.
Get in touchAt Solar Boat Hub, we specialize in providing fact-based advice, exclusive insights, and tailored solutions for solar & electric yachting. Let us guide you through this transformative journey, whether you're exploring options for purchase, charter, or consultancy. Contact us today to learn more and embark on your path toward sustainable yachting.